Unisphere, together with vCenter Server integration, makes storage management in a virtualized environment quite easy. EMC has delivered the VMware vStorage API for Array Integration (VAAI), allowing the VNX series to be fullz optimiyed for virtualiyed environments. This technologz offloads VMware storage-related functions from the server to the storage system, enabling more efficient use of server and network resources for increased performance and consolidation.
The VNX series also supports the VMware vStorage API for Storage Awareness (VASA), allowing the VNX storage capabilities to be mapped to vCenter Storage Profiles for creating virtual machines.
VMware ESXi servers connect to VNX block storage through FC, FCoE, iSCSI. The block storage is provisioned to the ESXi host for creating VMFS datastores for virtual machines or as a raw device-mapped (RDM) volumes for virtual machines. Note: ESXi servers can also access VNX file storage through NFS.
EMC VSI
EMC Virtual Storage Integrator (VSI) for VMware vSphere Unified Storage Management is a VMware feature designed to simplify storage administration of the EMC VNX. The feature enables VMware admins to provision new NFS and VMFS datastores, and RDM volumes directly from vSphere Client.
VAAI
The vStorage API for Arraz Integration (VAAI) is a VMware-based vendor neutral storage API. It is designed to offload specific storage operations to compliant storage arrays. The array thus provides a hardware acceleration of the ESXi storage operations. Offloading storage operations to the array reduces ESXi CPU, memory and storage fabric bandwidth consumption, thus enabling more of its compute power to be available for running virtual machines.
VAAI operations
- Array Accelerated Bulk Zero – Within a virtual disk file there is both used space (data) and empty space yet to be utilized. When a VM is cloned this “empty space” is also copied, which means that many additional SCSI operations are generated for, essentially, empty space. Block Zeroing allows for a reduced SCSI command operation set to be generated as the storage array is made responsible for zeroing large numbers of blocks without impacting the creating ESXi server. This is achieved by acknowledging the completion of the zero block write before the process has completed and then completing the process in the background.
- Full Copy – The creation of a Virtual Machine (VM) from a template is performed within the storage array by cloning the Virtual Machine from one volume to another, utilizing the array functionality and not the ESXi server’s resources.
- Hardware Locking – VMFS volume locking mechanisms are offloaded to the array and are implemented at the sub-volume level. This allows the more efficient use of shared VMFS volumes by VMware cluster servers by allowing multiple locks on a VMFS volume without locking the entire volume. The ATS operation atomically (non-interruptible) compares an on-disk sector to a given buffer, and, if the two are identical, writes new data into the on-disk sector. The ATS primitive reduces the number of commands required to successfully acquire an on-disk lock.
- Thin Provisioning – When a VM is deleted or migrated from a Thin LUN datastore, the space that was consumed is reclaimed to available space in the storage pool.
- Stun and resume – When a thin LUN runs out of space due to VM space consumption, the affected VM is paused to prevent it from being corrupted. The storage administrator is alerted to the condition so more storage can be allocated.
VASA
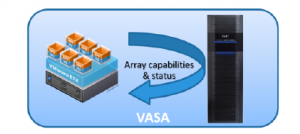
The VMware Aware Storage API (VASA) is a VMware-based vendor neutral storage API. VASA is a VMware specific feature and protocol and uses an out-of-band http level protocol to communicate with the storage environment.
It is designed for the storage array to provide its storage capabilities into VMware vCenter. The VNX will provide capabilities for its Storage Processors, LUNS, I/O ports and file systems. The array health status and space capacity alerts are also provided to vCenter.
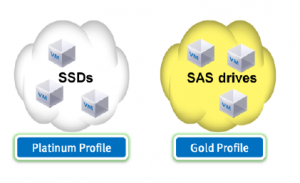
A key aspect of the API integration is the ability to create and use profiles for system resource configuration. In this case a Storage Profile can be defined for a specific VM need and then when performing vMotion or Cloning etc. a profile can be substituted for an actual target device.
The system will then chose a target of the same profile and will highlight the most suitable target based on free space for the target.
Storage profiles can also be associated with a datastore cluster when SDRS is enabled. When the profile is part of a datastore cluster, SDRS controls datastore placement.
Storage capabilities can also be used for other tasks such as new VM creation and VM migration. They provide the ability to match virtual machine disks with the appropriate class of storage to support application I/O needs for VM tasks such as initial placement, migration, and cloning.

One thought on “EMC VNX – Support for VMware”